By: Team AY1920S1-CS2103T-W13-3
- 1. Introduction
- 2. Quick Start
- 3. Command Format / Rules
- 4. Global Commands
- 4.1. Entering the various modes of StudyBuddyPro:
switch - 4.2. Viewing Help:
help - 4.3. Listing all current Tags in StudyBuddyPro :
taglist - 4.4. Listing all StudyBuddyPro items by their tag :
filterall - 4.5. Clearing specific feature’s data:
clear - 4.6. Clearing entire application’s data:
clear all - 4.7. Exiting the application:
exit - 4.8. Editing a tag:
edit tag(proposed in v2.0)
- 4.1. Entering the various modes of StudyBuddyPro:
- 5. Flashcard Feature
- 5.1. How to create a flashcard:
add - 5.2. Viewing a flashcard:
view - 5.3. Revealing a flashcard’s answer:
show - 5.4. Editing a flashcard:
edit(Coming in v2.0) - 5.5. How to view a list of all available flashcards:
list - 5.6. How to delete a flashcard:
delete - 5.7. How to enter the timetrial mode:
timetrial - 5.8. How to filter flashcards based on the tags provided:
filter - 5.9. Find out what flashcards to revise today, or ones you may have missed:
remind
- 5.1. How to create a flashcard:
- 6. Notes Feature:
- 7. CheatSheet Feature:
- 7.1. To auto-generate a Cheatsheet:
add - 7.2. To edit a Cheatsheet:
edit - 7.3. Deleting a Cheatsheet:
delete - 7.4. To view Cheatsheets:
view - 7.5. To view Cheatsheets of a Specific Tag:
show - 7.6. To list all Cheatsheets:
list - 7.7. Listing by tags:
filter - 7.8. Updating a Cheatsheet:
update(Coming in v2.0)
- 7.1. To auto-generate a Cheatsheet:
- 8. FAQ
- 9. Command Summary
1. Introduction
StudyBuddyPro is a student application that aims to simplify the hassle of revision by providing a suite of tools for effective revision.
StudyBuddyPro is optimized for students who prefer to work with a Command Line Interface (CLI) while still having the benefits of a Graphical User Interface (GUI).
Moreover, StudyBuddyPro comes geared with pre-loaded features specially catered for computing students. So whether you’re a computing student getting used to a CLI for the first time or if you’re a CLI expert who wants to reap the benefits of a fast typing speed, give StudyBuddyPro a try!
If you’re interested, head over to the Quick Start section to get started!
1.1. Callouts Signs
Do refer to the signs below that will be used across the documents for references. These will prove to be useful when you are reading this document.
|
Indicates information that are to be adhered as potential problems may be encountered if you are not careful. |
|
Indicates information that are crucial to understand so that you will be able to follow the flow of the document. Confusion may arise if you do not grasp the information here. |
|
Indicates information that are note-worthy. Do read them for more information and better understandings. |
|
Indicates additional information that are helpful. Fret not, tips can be good to know but are not vital. |
2. Quick Start
| Please ensure you have Java 11 or above installed before proceeding! |
-
Download the latest version of
StudyBuddyPro.jarhere. -
Place the file in the folder you want to set as the home directory. All data and miscellaneous files associated with StudyBuddyPro will be placed in this folder.
-
Double-click
StudyBuddyPro.jarto launch the application. The GUI should appear in a few seconds, and should look like the screen shown below. If not, please refer to the first question in the FAQ for help!Figure 1. GUI of StudyBuddyPro application displayed on startup -
Type a command in the command box execute it by pressing Enter. Typed commands will appear in the CLI highlighted in the purple box in the diagram above. Refer to the Command Summary section for a quick overview of all the available commands!
-
Output from the command will be shown in the boxes highlighted in orange and green in the diagram above. The green box is used to display a flashcard, note or cheatsheet while the orange box outputs feedback from commands.
| The blue box in the diagram above with the "Flashcards", "Notes" and "Cheatsheets" logo can be used to quickly check which mode you are in! Switching into a mode will highlight the relevant mode’s logo in an orange circle, as shown in this figure. |
3. Command Format / Rules
Things noted here are standardization of the User Guide. These points are absolute, unless stated otherwise in the specific section(s).
3.1. How to read the Command sections
-
Words in
UPPER_CASEare parameters to be supplied by the user. E.g.add t/TITLE→TITLEis a parameter which can be used asadd t/Midterm notes. -
Items indicated in square brackets are optional, unless specified. E.g
t/TITLE [tag/TAG]can be used ast/Midterm note tag/examor ast/Midterm. -
Items with
… after them can be used multiple times including zero times. E.g.[tag/TAG]…can be used astag/friend,tag/friend tag/family.
3.2. General rules for all commands
-
All commands are written in English.
-
Some command parameters are restricted to purely alphanumeric characters, while others are just required to not be blank.
-
Any indexes provided (denoted by '(index)' ) must be a positive integer (e.g. 1, 2, 3, …).
-
All flashcards, notes, and cheatsheets can have a maximum of 10 tags.
-
Only exact matches of any searches will be returned. E.g. "noted" will return "noted" but not "note" or "notes"
-
All searches, like
filter, are case insensitive. E.g. 'tag/cs2103t' will match 'tag/CS2103T' andfilter tag/importantwill matchfilter tag/IMPORTANT -
If multiple inputs are given for a particular field, only the last valid input for the field is taken, unless the field allows multiple inputs. E.g.
add q/this is a question a/this is an answer q/another question→ the application will only take inq/another questionas the input field forquestion.
4. Global Commands
Global commands in StudyBuddyPro are commands that can be called regardless of which mode the user is currently in.
4.1. Entering the various modes of StudyBuddyPro: switch
Upon startup, you will be prompted to enter one of the modes before you can proceed.
4.1.1. Getting into Flashcard mode: switch fc
Switches the user to Flashcard mode regardless of where the user is.
Format: switch fc
4.1.2. Getting into Notes function: switch notes
Brings the user to Notes mode regardless of where the user is.
Format: switch notes
4.1.3. Getting into CheatSheet function: switch cs
Brings the user to CheatSheet mode regardless of where the user is.
Format: switch cs
4.2. Viewing Help: help
A pop-up dialog box will display a URL link to a help document.
Format: help
4.3. Listing all current Tags in StudyBuddyPro : taglist
Displays to you a full list of all tags you have currently in StudyBuddyPro.
Format: taglistExpected output:
Here are all the tags in StudyBuddyPro.
Listing all tags :
[cs2100] | flashcards : 0 notes : 3 cheatsheets : 1
[cs2101] | flashcards : 6 notes : 2 cheatsheets : 1
[cs2104] | flashcards : 20 notes : 8 cheatsheets : 3
[math] | flashcards : 10 notes : 2 cheatsheets : 1
[pipelining] | flashcards : 1 notes : 5 cheatsheets : 2-
The user can make use of taglist, to quickly see which tag they would like to view.
-
The user is able to view how many flashcards, notes and cheatsheets respectively there are in each tag.
-
The list of tags is also automatically sorted alphabetically.
-
If there are no longer any items with the specified tag, the tag will be removed from this list.
4.4. Listing all StudyBuddyPro items by their tag : filterall
Lists all StudyBuddyPro items with matching tags in the application.
|
Format: filterall tag/TAG [tag/TAG]...
Let’s say the user wishes to view the definition of pipelining. Pipelining is taught in CS2100, a Computer Organization module taught in the School of Computing at NUS. Hence, the user can make use of filterall to find all flashcards, cheatsheets and notes that are tagged “CS2100”. Note that for simplicity, all tags will be converted to lowercase upon input. Hence, ‘CS2100’ will be read as ‘cs2100’ by our application.
Example usage:
filterall tag/CS2100
Expected output:
Listing the whole StudyBuddyPro after filtering by tag(s) :
CS2100
Flashcard: 6.
Question: What is 101 Binary in its Decimal form?
Answer: 5
Title: BinaryQn
Tags: [cs2100]
CheatSheet: 7.
Title: cs2100 stuff
Tags: [cs2100]
Contents: [ 1. Pipelining is a process where a processor executes multiple processes simultaneously.]
[ 2. Question: What is 101 Binary in its Decimal form?; Answer: 5 ]
Note: 5.
Title: Pipelining Definition
Content: Pipelining is a process where a processor executes multiple processes simultaneously.
Tags: [cs2100]
Note Fragment: 6-2.
Title: About Notes
Content: highlighted
Tags: [cs2100]| 'Note Fragments' (as seen in the example above) are described further in the Notes section (see Section 6.1). |
The user is also able to specify a multiple number of tags. For example,
filterall tag/CS2100 tag/difficult
will list all items that match all of the specified tags.
4.5. Clearing specific feature’s data: clear
| Proceed with care when using this function!! Using the clear function will IMMEDIATELY clear ALL of the data from the mode you are in! |
Clears the data in a specific feature. Depending on the mode that the user is in, the clear command will only
clear the specific feature’s data.
Example usage:
clear
Expected output:
Cleared all flashcards/notes/cheatsheets!
4.6. Clearing entire application’s data: clear all
| Proceed with care when using this function!! Using the clear function will IMMEDIATELY clear ALL of the data in StudyBuddyPro! |
Clears all the data in the application.
Example usage:
clear all
Expected output:
Cleared the entire StudyBuddyPro!
4.7. Exiting the application: exit
Checks if there are any remaining flashcards to revise for the day or overdue flashcards to revise before exiting the application.
Example usage:
exit
If there are flashcards due for revision today but no overdue flashcards:
Expected output:
Are you sure you want to exit? You still have the following flashcards overdue or left
to revise for today:
Here are the flashcards due today:
1. Math Question 1 - What is 2 x 2?
Type 'exit' again to exit the application!If there are no flashcards due for revision today but there are overdue flashcards:
Expected output:
Are you sure you want to exit? You still have the following flashcards overdue or left
to revise for today:
Here are your overdue flashcards:
1. Math Question 1 - What is 2 x 2? (Was due on 2019-10-30)
Type 'exit' again to exit the application!If there are both flashcards due for revision today and overdue flashcards:
Expected output:
Are you sure you want to exit? You still have the following flashcards overdue or left
to revise for today:
Here are the flashcards due today:
1. Math Question 1 - What is 2 x 2?
Here are your overdue flashcards:
1. Math Question 2 - What is 3 x 2? (Was due on 2019-10-30)
Type 'exit' again to exit the application!-
After any of the 3 scenarios above user can override the warning by entering the
exitcommand again. -
If no remaining or overdue flashcards for revision found, application exits immediately.
-
The user can use this feature to alleviate worries that they may forget to revise the relevant content for the day - StudyBuddyPro will always double-check for you!
4.8. Editing a tag: edit tag (proposed in v2.0)
Edits a tag by the specified index.
Format: edit tag/CURRENT tag/NEW
Example usage:
edit tag/midterm tag/finals
Expected output:
Tag edited!
All items and contents in StudyBuddy tagged ‘midterm’ is replaced with tag ‘finals’.This allows the user to easily modify the tags of all the items with a single command.
For instance, if the user has items that are tagged [cs2100] and [midterm], and the user wishes to make use of such items to include in a cheatsheet for CS2100 finals, the user can input
edit tag/midterm tag/finals
to conveniently change, for instance, all notes tagged with [midterm] to be tagged with [finals].
This then allows the user to more conveniently generate a cheatsheet for his/her final exams.
5. Flashcard Feature
Sick and tired of cramming all your revision at the last minute? Why not give our Flashcards feature a try! This feature can help you create your very own flashcards to help you consistently revise. With our built-in reminder features and timetrial modes to test yourself, use this feature and be on track to better revising habits today!
|
Good news - StudyBuddyPro comes with some preloaded flashcards, specially catered for you as a computing student! Be sure to take a look! Psst - here’s a hint for our more tech-savvy users: You can delete your flashcards.json file in the StudyBuddyPro data folder to restore these default flashcards at any time. Of course, your current flashcards will be deleted as well! |
|
All the operations in this section assume that the user is in the flashcard mode. To be sure
you are flashcard mode, please ensure you used the |
5.1. How to create a flashcard: add
Adds a flashcard from user input question <QUESTION> and answer <ANSWER>.
Format: add q/QUESTION a/ANSWER t/TITLE [tag/TAG]...
Example usage:
add q/What is 100 Binary in its Decimal form? a/4 t/Binary Stuff tag/CS2100
Expected output:
New flashcard added: Title: Binary Stuff
Tags: [cs2100]5.2. Viewing a flashcard: view
Displays flashcard <FLASHCARD_INDEX> to user without answer.
Format: view (index)
Example usage:
view 6
will view the Flashcard at Index 6.
Expected output:
Viewing flashcard:
Title: BinaryQn
Question: What is 101 Binary in its Decimal form?
Tags: [cs2100]5.3. Revealing a flashcard’s answer: show
Displays the answer of the flashcard currently loaded.
Format: show
Example usage:
show
Expected output:
Flashcard answer loaded5.4. Editing a flashcard: edit (Coming in v2.0)
Edits a flashcard’s question, answer, title, or tags. The flashcard will be referred to by their original title
ORIGINAL_TITLE.
Format: edit ORIGINAL_TITLE [q/NEW_QUESTION] [a/ANSWER] [t/TITLE] [tag/TAG]...
-
At least one of the optional fields must be provided.
Example usage:
edit IntelliJ Question 1 q/What is the meaning of SLAP? a/Single Layer of Abstraction Principle t/SE Question 1
Expected output:
Edited flashcard:
Title: SE Question 1
Question: What is the meaning of SLAP?
Tags: [cs2100]-
Notice how the fields that are not edited retain their original information. For example, the tag field was not changed and so the original cs2100 tag was retained.
-
Multiple fields can be edited at the same time. In the example, the question, answer and title fields were all edited at once.
5.5. How to view a list of all available flashcards: list
Lists all flashcards.
Format: list
Example usage:
list
Expected output:
Listing all flashcards:
1. Title: Pipelining Question 1
Tags: [cs2100]5.6. How to delete a flashcard: delete
Deletes the flashcard by <FLASHCARD_INDEX> provided by the user.
The user will be prompted again to confirm their deletion.
Format: delete (index)
Example usage:
delete 6
Expected output:
Are you sure you would like to delete the following flashcard?
Title: Binary Question 1
Tags: [cs2100]
Please use `delete 6` again to confirm your deletion..
Inputting invalid commands will NOT offer another prompt to the user.
For example, calling delete 3, then an invalid command and then delete 3 again will immediately delete the 3rd item without a prompt.
|
Upon keying in delete 6 again, then the flashcard will be deleted.
Expected output:
Deleted Flashcard: Title: Binary Question 1
Tags: [cs2100]
If you were viewing a flashcard and then delete it, it will still remain shown as the last
loaded flashcard in the GUI. Use the view command to view another flashcard instead and
refresh the GUI!
|
5.7. How to enter the timetrial mode: timetrial
Starts a time trial for flashcards with specified tags.
Format: timetrial TAG...
Example usage:
timetrial cs2103tuml hard
Expected output:
Time trial startedAll of the flashcards containing the specified tags will be then displayed sequentially in the activity below.
-
At least one tag must be specified.
-
If more than one tag is specified, selects all flashcards that contains all of the specified tags.
-
Default <TIME> will be 5 seconds.
-
Answer will be flashed for 3 seconds.
-
If a flashcard command (other than
show) is inputted during the time trial, the time trial will be terminated and the inputted command will be executed. -
Executing
showwill reveal the answer of the flashcard in advance, but will not terminate the time trial.
5.8. How to filter flashcards based on the tags provided: filter
-
Filters the flashcard library by the user specified tag(s).
-
The user must specify at least one tag.
-
The user is able to specify multiple tags.
-
Flashcards that match all of the specified tags will be displayed.
Format: filter tag/TAG [tag/TAG]...
Example usage:
filter tag/difficult
Expeted output:
Filter flashcards by tag(s) :
[difficult]
8. Question: What is 1+1?
Title: Basic addition
Tags: [difficult]
10. Question: What is 2x3?
Title: Maths
Tags: [difficult][important]
5.9. Find out what flashcards to revise today, or ones you may have missed: remind
This feature helps the user check which flashcards are due for revision today and which flashcards overdue for revision. StudyBuddyPro automatically sets the date the flashcard should next be viewed at for optimal learning. These increments also scale with time i.e. newer flashcards will have to be viewed more often.
| Be sure to check in everyday to see which flashcards you have due! |
StudyBuddyPro only marks a flashcard as revised and removes it from the due and
overdue flashcard list when you see the flashcard’s answer not just its question! For
example, simply using the view command without the show command to reveal the flashcard’s
answer will not trick the system. Sorry, it’s for your own good!
|
Example usage:
remind
If no flashcards due for revision today and no overdue flashcards:
Expected output:
Well done - No due or overdue flashcards!If there are flashcards due for revision today but no overdue flashcards:
Expected output:
Here are the flashcards due today:
1. Math Question 1 - What is 2 x 2?If there are no flashcards due for revision today but there are overdue flashcards:
Expected output:
Here are your overdue flashcards:
1. Math Question 1 - What is 2 x 2? (Was due on 2019-10-30)If there are both flashcards due for revision today and overdue flashcards:
Expected output:
Here are the flashcards due today:
1. Math Question 1 - What is 2 x 2?
Here are your overdue flashcards:
1. Math Question 2 - What is 3 x 2? (Was due on 2019-10-30)6. Notes Feature:
Have too many things memorized in your head, with nowhere to write them down? Tired of jotting down thoughts in loose text files on your computer? Then give our Notes a try! Quick and easy to use, they help you keep track of all the loose bits of knowledge that you want to keep around but don’t have the brain space to keep! Take note of these Notes and studying will be a breeze!
|
All the operations in this section assume that the user is in the notes mode. To be sure
you are in the notes mode, please ensure you used the |
6.1. To create a note: add
Adds a note from user input with title TITLE and content CONTENT, that you can conveniently access later. The title of the note cannot be a duplicate
of an existing note title.
Format: add t/TITLE c/CONTENT [tag/TAG]...Example usage:
add t/Pipelining Definition c/Pipelining is a process where a processor executes multiple processes simultaneously. tag/cs2100Expected output:
New note added:
Title: Pipelining Definition
Content: Pipelining is a process where a processor executes multiple processes simultaneously.
Tags: [cs2100]
The added Note has no detected note fragment tags!More advanced usage: This is where our Notes feature stands out from the others! Tagging of note fragments is also supported. The note fragment tagging is added at the same time as the note is created.
Note fragments can be visualised as a form of highlighting your notes. Its tags are added with content FRAGMENT_CONTENT, at least one tag
FRAGMENT_TAG, and any number of additional tags ADDITIONAL_FRAGMENT_TAG:
Format (within CONTENT): /* C/FRAGMENT_CONTENT TAG/FRAGMENT_TAG [TAG/ADDITIONAL_FRAGMENT_TAG]... */| The format for note fragment content is 'C/', not 'c/', and the format for note fragment tags is 'TAG/', not 'tag/'. |
| If the format is not followed correctly, the note fragment tag will simply not be added (but the note will still be added). StudyBuddyPro will assume that the user has typed the tags correctly. |
In the following example, two note fragment tags are added to the same note fragment:
Example usage:
add t/About Notes c/Notes can be /* C/highlighted TAG/highlight TAG/important */ if needed. tag/aboutExpected output:
New note added:
Title: About Notes
Content: Notes can be /* C/highlighted TAG/highlight TAG/important */ if needed.
Tags: [about]
Note fragment tags detected:
Title: About Notes
Content: highlighted
Tags: [important][highlight]This adds a note with content "Notes can be highlighted if needed.", and a note fragment tag with content "highlighted" and two tags "cs2100" and "important".
| The spaces around the syntax elements of '/*', 'C/' etc are part of the syntax. For example, if a note fragment tag looks like this: '/* C/highlighted TAG/important */if needed', then the resultant Note will look like this: 'highlightedif needed'. |
Multiple note fragment tags are allowed. These do not interfere with the other tags of the Note.
| Overlapping note fragment tags are not allowed. |
Note fragment tags can be used for filtering notes (see Section 6.6), or filtering globally (see Section 4.3).
For a clearer visualization of note fragments, compare the view (see Section 6.3) and viewraw (see Section 6.4)
commands.
|
6.2. To delete a note: delete
Simply get rid of any unwanted notes and make your life easier using delete.
Deletes the note of index NOTE_INDEX.
The user will be prompted once to confirm their deletion.
Format: delete (index)Example usage:
delete 3Expected output:
Are you sure you would like to delete the following note?
Title: About Notes
Content: Notes can be /* C/highlighted TAG/highlight TAG/important */ if needed.
Tags: [about]
Please use `delete 3` again to confirm your deletion.Upon using delete 3 again, then the note will be deleted.
Deleted note:
Title: About Notes
Content: Notes can be /* C/highlighted TAG/cs2100 TAG/important */ if needed.
Tags: [about]
Inputting invalid commands will NOT offer another prompt to the user.
For example, calling delete 3, then an invalid command and then delete 3 again will immediately delete the 3rd item without a prompt.
|
6.3. To view a note: view
Views the note of index NOTE_INDEX. If the note contains any note fragment tags, those tags will be hidden.
To view the note with its note fragment tags, use the viewraw command instead (see Section 6.4).
|
Format: view (index)Example usage:
view 3Expected output:
Viewing note:
Title: About Notes
Content: Notes can be highlighted if needed.
Tags: [about]6.4. Viewing a raw note: viewraw
Views the note of index NOTE_INDEX. The note is shown exactly as written, including all note fragment tags.
Format: viewraw (index)Example usage:
viewraw 3Expected output:
Viewing raw note:
Title: About Notes
Content: Notes can be /* C/highlighted TAG/cs2100 TAG/important */ if needed.
Tags: [about]6.5. To list all notes: list
Lists all notes found in StudyBuddyPro.
Format: listExpected output:
A complete list of all notes currently in StudyBuddyPro.Example output:
Listing all notes:
1.
Title: Pipelining Definition
Content: Pipelining is a process where a /* C/processor TAG/mips */ executes multiple processes simultaneously.
Tags: [cs2100]
2.
Title: UML Diagrams
Content: UML Diagrams help with visualizing project structure.
Tags: [cs2103t]
Notes will be labeled with indices '1', '2' etc. Note fragment tags will not be listed along with the notes. To
visualize specific note fragment tags, use the filter command (see Section 6.6).
|
6.6. Filtering by tags: filter
filter allows you to quickly search for your notes by their specified tags.
-
Filters the note library by the user specified tag(s).
-
The user must specify at least one tag, and can specify multiple tags.
-
Notes that match all of the specified tags will be displayed.
-
Note fragment tags containing all of the specified tags will also be displayed, even if their parent note is not tagged.
Format: filter tag/TAG [tag/TAG]...Example usage:
filter tag/difficultExpected output:
Filter notes by tag(s) :
[difficult]
2. Title: Tough Math
Content: 1 + 2 is 3.
Tags: [difficult]
4. Title: MA1521 Chapter 5
Content: dy/dx = 0 is turning point of bellcurve.
Tags: [difficult][MA1521]
5-1. Title: CS2103T
Content: sequence diagram
Tags: [difficult][diagram]| Notes will be labeled with indices '1', '2' etc. Note fragment tags will be labeled with '1-1', '1-2', '2-1' etc. '5-1' means 'the first note fragment tag in the fifth note'. |
6.7. Editing a note: edit (Coming in v2.0)
Edits a note’s title, content, or tags. The note will be referred to by their original title ORIGINAL_TITLE.
-
The user can specify one of the optional fields to edit.
Format: edit ORIGINAL_TITLE [t/TITLE] [c/CONTENT] [tag/TAG]...Example usage:
edit Pipelining Definition t/Pipelined Definition tag/cs2100finalsExpected output:
Edited Note:
Title: Pipelined Definition
Content: Pipelining is a process where a processor executes multiple processes simultaneously.
Tags: [cs2100finals]7. CheatSheet Feature:
Ever spent countless of hours rummaging through your notes just to dig up important information to add to your cheatsheet for your exams? Ever feared that you might accidentally miss out on important information to add to your cheatsheet? Fret not! Our very own cheatsheet feature of StudyBuddyPro is here to help you auto-generate your important information, and to simply, save the day.
|
All the operations in this section assume that the user is in the cheatsheet mode. To be sure
you are in the cheatsheet mode, please ensure you used the |
7.1. To auto-generate a Cheatsheet: add
Adds a cheatsheet from user input title <TITLE> and content <CONTENT>. Voila! To your convenience, flashcards and notes in StudyBuddyPro that have the specified tag upon creation of the cheatsheet will be used as contents.
Format: add t/TITLE [tag/TAG]...
Example usage:
add t/CS2100 Midterm CheatSheet tag/cs2100midterm
|
Assuming that there is a flashcard object with the tag "cs2100midterm" |
Expected output:
New cheatsheet added:
Title: CS2100 Midterm CheatSheet
Tags: [cs2100midterm]
1 content(s) have been successfully generated from the other modes.7.2. To edit a Cheatsheet: edit
Oh no! It appears that you might have accidentally misspelled something during creating a cheatsheet. Fret not, edit allows you to edit a cheatsheet’s title or remove tag or content by a specified <CHEATSHEET_INDEX>. At least one of the optional fields must be specified to edit.
Format: edit (index) [t/TITLE] [tag/TAG]...
|
Example CheatSheet of index 8:
Title: cs2100 cheatsheet
Tags: [cs2100finals][formula]
Contents: [ 1. Question: What is 110 Binary in its Decimal Form?; Answer: 6 ]
[ 2. 10 + 10 = 20]
Example usage:
edit 8 t/cs2100 final cheatsheet tag/formula
Expected output:
Edited Cheatsheet:
Title: cs2100 final cheatsheet
Tags: [cs2100finals]|
The actual implementation does not show the contents in the feedback box. Please do use |
7.3. Deleting a Cheatsheet: delete
Deletes a cheatsheet by the specified index.
The user will be prompted once to confirm their deletion.
Format: delete (index)
Example usage:
delete 8
Expected output:
Are you sure you would like to delete the following cheatsheet?
Title: CS2100 Finals CheatSheet
Tags: [finalcheatsheet]
Please use `delete 8` again to confirm your deletion.Upon hitting enter, then the specified cheatsheet will be deleted.
Expected output:
Deleted Cheatsheet:
Title: CS2100 Finals CheatSheet
Tags: [finalcheatsheet]
Inputting invalid commands will NOT offer another prompt to the user.
For example, calling delete 3, then an invalid command and then delete 3 again will immediately delete the 3rd item without a prompt.
|
7.4. To view Cheatsheets: view
Views a cheatsheet and its contents by the specified index.
Format: view (index)
Example CheatSheet of index 1:
Title: cs2100 cheatsheet
Tags: [cs2100finals][important]
Contents: [ 1. Question: What is 110 Binary in its Decimal Form?; Answer: 6 ]
[ 2. 10 + 10 = 20]
Example usage:
view 1
Expected output:
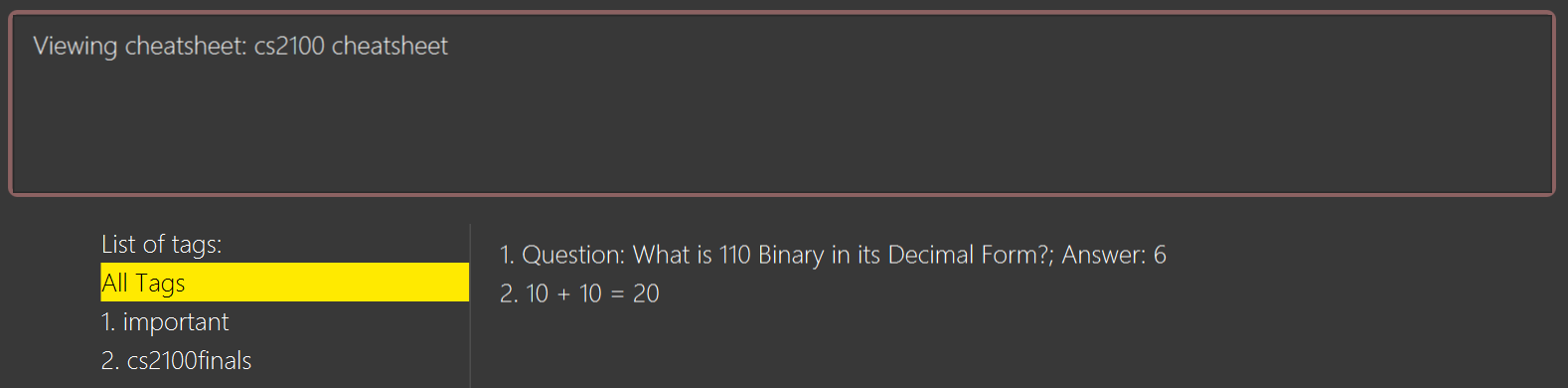
view 1 expected outputThe above screenshot shows the cheatsheet with index 1 in the GUI of StudyBuddyPro.
7.5. To view Cheatsheets of a Specific Tag: show
Views a cheatsheet’s content for a specified tag. User must be in a view command before using show command.
Format: show (index)
|
Assuming user is in the |
Example usage:
show 1
Expected output:

show 1 expected outputThe above screenshot shows the cheatsheet’s content with tag index 1 in the GUI of StudyBuddyPro.
|
Currently, cheatsheets only allow contents that match all the specified tags. Hence, |
7.6. To list all Cheatsheets: list
Lists all cheatsheets found in StudyBuddyPro.
Format: list
Example output: Listing all cheatsheets: 1. Title: CS2100 midterms Tags: [cs2100][midterms] 2. Title: ma1521 finals Tags: [finals][ma1521]
7.7. Listing by tags: filter
Want to quickly acccess your items? filter helps to list the cheatsheet library by the user specified tag(s).
|
Format: filter tag/TAG [tag/TAG]...
Example usage:
filter tag/difficult
Expected output:
Filter cheatsheet by tag(s) :
[difficult]
2. Title: Tough Math
Tags: [difficult][math]
7. Title: MA1521 Chapter 5
Tags: [difficult]
-
Contents of the cheatsheet will not be displayed during filter.
-
Use the view command instead, the view the contents of the cheatsheet. (refer to section 7.4)
7.8. Updating a Cheatsheet: update (Coming in v2.0)
Ever wanted to re-use your midterm cheatsheet by adding more contents into it and then use it for your final examinations?
Our update feature updates cheatsheet’s contents by a specified <CHEATSHEET_INDEX>. Tags specified are added into the list of tags for the cheatsheet if it not already exist.
|
This command may overwrite any customization of contents done prior to it as the cheatsheet’s contents will be regenerated. |
Format: update (index) [tag/TAG]...
Example CheatSheet of index 8:
Title: cs2100 cheatsheet Tags: [cs2100finals] Contents: [ 1. Question: What is 110 Binary in its Decimal Form?; Answer: 6 ]
Example usage 1:
update 8
Expected output:
Updated Cheatsheet:
Title: cs2100 final cheatsheet
Tags: [cs2100finals]
Contents: [ 1. Question: What is 110 Binary in its Decimal Form?; Answer: 6 ]
[ 2. Binary is in bits of 1 and 0.]|
The actual implementation does not show the contents in the feedback box. Please do use |
Example usage 2:
update 8 tag/formula
Expected output:
Updated Cheatsheet:
Title: cs2100 final cheatsheet
Tags: [cs2100finals][formula]
Contents: [ 1. Question: What is 110 Binary in its Decimal Form?; Answer: 6 ]
[ 2. 10 + 10 = 20]|
The actual implementation does not show the contents in the feedback box. Please do use |
Updated Cheatsheet:
Title: cs2100 final cheatsheet
Tags: [cs2100finals][formula]
Contents: [ 1. Question: What is 110 Binary in its Decimal Form?; Answer: 6 ]
[ 2. 10 + 10 = 20]
8. FAQ
Q: Help! Double-clicking StudyBuddyPro.jar does not launch the application - what
should I do?
A: Trying running the application from the command line using the following command:
java -jar StudyBuddyPro.jar. Windows users can use the Command Prompt application to
do this while Mac users can use the Terminal application.
Q: When I minimise the application, the entire application has shrunk and now it is gone! Help!
A: Currently our application do not allow diagonal or vertical resizing of the it. It is best not to resize the application at all and leave it as the maximized mode. For the this problem, we suggest that you try to maximise the application from the task manager or try to split the screen with another application so that StudyBuddyPro will resize back to normal. If the mentioned solutions fail, please do download StudyBuddyPro again!
Q: The preloaded deck of flashcards is overdue for revision and StudyBuddyPro says the last viewed date for
those preloaded flashcards was when I first opened StudyBuddyPro, even though I never even
viewed those flashcards! How is this possible?
A: StudyBuddyPro assumes all the default flashcards will be viewed when the application
was first opened. Aren’t you curious to see what we collated for you?
9. Command Summary
9.1. Global Commands (Can be executed in any mode)
-
Switch :
switch MODE
e.gswitch fc -
Filter All :
filterall tag/TAG…
e.gfilterall tag/cs2103tuml tag/difficult -
List tags :
taglist -
Help :
help -
List :
list -
Exit :
exit
9.2. Flashcard Commands
-
Add :
add q/QUESTION a/ANSWER t/TITLE [tag/TAG]…
e.g.add q/What is 100 Binary in its Decimal form? a/4 t/Binary Stuff tag/CS2100 -
Delete :
delete INDEXe.gdelete 1 -
Filter :
filter tag/TAG…
e.gfilter cs2103tuml -
Time Trial :
timetrial TAG…
e.gtimetrial cs2103t uml -
View :
view INDEX
e.gview 1 -
List :
list -
Show :
show -
Remind :
remind
9.3. Note Commands
-
Add :
add t/TITLE c/CONTENT tag/TAG…
e.g.add t/Pipelining Definition c/Pipelining is a process where a processor executes multiple processes simultaneously. tag/cs2100 -
Delete :
delete INDEXe.gdelete 1 -
View :
view INDEX
e.gview 1 -
Viewing a raw note :
viewraw INDEX
e.gviewraw 3 -
Filter :
filter tag/TAG…
e.gfilter tag/hard tag/cs2100 -
List :
list
9.4. CheatSheet Commands
-
Add :
add t/TITLE [tag/TAG]…
e.g.add t/CS2100 Midterm CheatSheet tag/cs2100midterm -
Delete :
delete INDEXe.gdelete 1 -
Edit :
edit INDEX t/TITLE tag/TAG…
e.gedit 8 t/cs2100 final cheatsheet tag/formula -
Show :
show INDEX
e.gshow 4 -
View :
view INDEX
e.gview 1 -
Filter :
filter tag/TAG…
e.gfilter tag/hard tag/cs2100 -
List :
list